Architecture sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. From the grandeur of ancient civilizations to the sleek designs of modern times, architecture is a fascinating blend of art, culture, and innovation.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of architectural design, history, and sustainability, we uncover a world where creativity meets functionality to shape the way we live and interact with our surroundings.
Definition of Architecture

Architecture is the art and science of designing and constructing buildings and other physical structures. It involves creating spaces that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing. Architects use their creativity and technical knowledge to design structures that meet the needs of the people who will use them.
Types of Architecture Styles
- 1. Classical Architecture: Characterized by symmetry, proportion, and ornate detailing, influenced by ancient Greek and Roman designs.
- 2. Gothic Architecture: Known for its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, commonly seen in cathedrals and churches.
- 3. Modern Architecture: Emphasizes simplicity, clean lines, and the use of new materials such as glass and steel, popularized in the 20th century.
- 4. Islamic Architecture: Features intricate geometric patterns, domes, and minarets, reflecting Islamic cultural and religious values.
- 5. Asian Architecture: Includes styles such as Chinese, Japanese, and Indian architecture, each with distinct characteristics and building techniques.
Importance of Architecture
Architecture plays a crucial role in shaping societies and cultures. It not only provides functional spaces for people to live and work but also reflects the values and aspirations of a community. Well-designed buildings can inspire creativity, foster a sense of identity, and contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of a city or region.
Architectural Elements

Architectural elements are essential components of design that define the aesthetics, functionality, and overall character of a structure. These elements encompass form, function, materials, and space, each playing a crucial role in shaping the built environment.
Traditional vs. Modern Architectural Elements
Traditional architectural elements often emphasize intricate ornamentation, symmetry, and craftsmanship, reflecting cultural and historical influences. In contrast, modern architectural elements focus on simplicity, minimalism, and innovative use of materials and technology.
- Form:Traditional architecture may feature elaborate facades and decorative detailing, while modern design tends towards clean lines and geometric shapes.
- Function:Traditional buildings were often designed for specific purposes like religious or communal use, whereas modern structures prioritize efficiency, sustainability, and flexibility.
- Materials:Traditional architecture relied on locally sourced materials like stone, wood, and clay, while modern architecture explores new materials such as glass, steel, and concrete for their aesthetic and structural properties.
- Space:Traditional buildings typically had defined spatial hierarchies and compartmentalized layouts, whereas modern architecture embraces open floor plans, natural light, and fluid spatial configurations.
Contribution to Aesthetics and Functionality
Architectural elements play a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal and functionality of a structure. The careful integration of form, function, materials, and space results in a harmonious design that not only pleases the eye but also serves the needs of its users.
Architectural History

Architecture has a rich history that spans across civilizations and centuries, evolving and adapting to various cultural, social, and technological influences. From the monumental structures of ancient civilizations to the innovative designs of contemporary architects, the history of architecture is a fascinating journey through time.Throughout history, significant architectural movements have emerged, shaping the way buildings are designed and constructed.
These movements have been influenced by a variety of factors, including technological advancements, cultural shifts, and artistic trends. Each movement reflects the values and aspirations of the society in which it originated, leaving a lasting impact on the built environment.Historical events and cultural shifts have played a crucial role in shaping architectural styles over time.
Wars, revolutions, and economic changes have all had an impact on the way buildings are designed and used. Additionally, the exchange of ideas and influences between different cultures has led to the development of unique architectural styles that blend tradition with innovation.
Ancient Civilizations
Architecture in ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome was characterized by grandeur and symbolism. The pyramids of Egypt, the Parthenon in Greece, and the Colosseum in Rome are iconic examples of architectural achievements that continue to inspire awe and admiration today.
- Ancient Egyptian architecture was focused on monumental structures like pyramids and temples, built to honor gods and pharaohs.
- Greek architecture emphasized harmony, balance, and proportion, with the use of columns and pediments in temple design.
- Roman architecture was known for its engineering feats, such as the arch, vault, and dome, seen in structures like the Colosseum and the Pantheon.
Modernism and Bauhaus Movement
The modernist movement, which emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, rejected traditional ornamentation in favor of simplicity, functionality, and the use of new materials like glass and steel. The Bauhaus movement, founded in Germany in the 1920s, emphasized the integration of art, craft, and technology in design.
- Modernist architects like Le Corbusier and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe championed the use of clean lines, open spaces, and geometric forms in their designs.
- The Bauhaus school, led by Walter Gropius, promoted the idea of creating total works of art that combined architecture, design, and craftsmanship.
Postmodernism and Deconstructivism
Postmodernism, which emerged in the late 20th century, challenged the principles of modernism by reintroducing historical references, ornamentation, and playful elements in design. Deconstructivism, influenced by postmodernism, sought to break away from traditional forms and create fragmented, non-linear structures.
- Postmodern architects like Robert Venturi and Michael Graves embraced eclecticism and irony in their designs, incorporating historical styles and pop culture references.
- Deconstructivist architects like Frank Gehry and Zaha Hadid pushed the boundaries of form and structure, creating dynamic and unconventional buildings that defy traditional conventions.
Sustainable Architecture
Sustainable architecture focuses on creating buildings that are environmentally responsible, resource-efficient, and energy-efficient throughout their lifecycle. It aims to minimize the negative impact of construction on the environment while maximizing the health and wellbeing of occupants.
Principles of Sustainable Architecture
- Energy efficiency: Designing buildings to reduce energy consumption and utilize renewable energy sources.
- Water conservation: Implementing systems for rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling.
- Material selection: Using sustainable and recycled materials to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact.
- Site planning: Designing structures that work harmoniously with the surrounding environment and ecosystems.
- Indoor air quality: Ensuring proper ventilation and using non-toxic materials for healthier indoor spaces.
Examples of Sustainable Architecture Projects
- The Edge in Amsterdam, Netherlands: This building is considered the greenest office building in the world, utilizing solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient design.
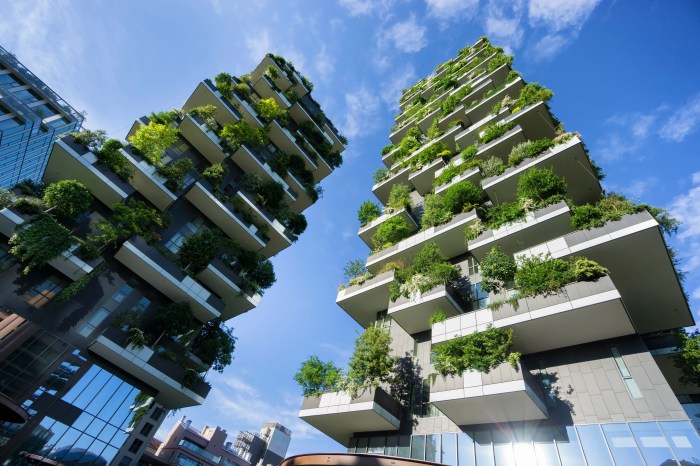
- Bosco Verticale in Milan, Italy: These twin towers are covered in plants, providing natural insulation, reducing energy consumption, and improving air quality.
- One Central Park in Sydney, Australia: Featuring vertical gardens and solar panels, this residential complex showcases sustainable living in an urban setting.
Importance of Sustainability in Modern Architecture
Sustainability is crucial in modern architectural practices as it not only reduces the environmental impact of buildings but also contributes to the overall wellbeing of individuals and communities. By integrating eco-friendly design principles, architects can create spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also promote a healthier and more sustainable future for generations to come.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, architecture stands as a testament to human ingenuity and creativity, weaving together the threads of our past, present, and future. It is not just about buildings and structures, but a reflection of our values, aspirations, and collective identity.
As we continue to push the boundaries of architectural possibilities, we embark on a journey of discovery, innovation, and transformation that will leave an indelible mark on generations to come.
Essential Questionnaire
What is sustainable architecture?
Sustainable architecture focuses on eco-friendly design principles that minimize environmental impact and promote energy efficiency in building structures.
How do architectural elements contribute to a structure’s aesthetics?
Architectural elements such as form, materials, and space play a crucial role in defining the visual appeal and overall look of a building, enhancing its aesthetic value.
What are some examples of significant architectural movements?
Architectural movements like Art Nouveau, Modernism, and Postmodernism have left a lasting impact on design trends and architectural practices over the years.